The Potential Economic Impacts of Various Debt Ceiling Scenarios
Summary
New analyses by both the Congressional Budget Office and the U.S. Department of the Treasury suggest the United States is rapidly approaching the date at which the government can no longer pay its bills, also known as the “X-date.” History is clear that even getting close to a breach of the U.S. debt ceiling could cause significant disruptions to financial markets that would damage the economic conditions faced by households and businesses. Real time data, shown below, indicate that markets are already pricing in political brinkmanship related to Federal government default through higher risk premia.
An actual breach of the U.S. debt ceiling would likely cause severe damage to the U.S. economy. Analysis by CEA and outside researchers illustrates that if the U.S. government were to default on its obligations—whether to creditors, contractors, or citizens—the economy would quickly shift into reverse, with the depth of the losses a function of how long the breach lasted. A protracted default would likely lead to severe damage to the economy, with job growth swinging from its current pace of robust gains to losses numbering in the millions.
In other words, defaulting on our government’s debt could reverse the historic economic gains that have been achieved since the president took office: an unemployment rate near a 50-year low, the creation of 12.6 million jobs, and robust consumer spending that has consistently powered a solid, reliable growth engine, supported by paychecks from the strong job market and healthy household balance sheets.
Because the government would be unable to enact counter-cyclical measures in a breach-induced recession, there would be limited policy options to help buffer the impact on households and businesses. The ability of households and businesses, especially small businesses, to borrow through the private sector to offset this economic pain would also be compromised. The risks engendered by the default would cause interest rates to skyrocket, including those on the financial instruments that households and businesses use—Treasury bonds, mortgages, and credit card interest rates.
Potential impacts of approaching the debt ceiling
There is no historical precedent for the U.S. government passing the X-date and breaching its debt ceiling without Congress raising or suspending the statutory limit on federal debt. Nevertheless, there is broad consensus amongst economists that such an event would generate an entirely-avoidable economic catastrophe.
For example, Brookings Institution analysts Wendy Edelberg and Louise Sheiner recently argued that “Worsening expectations regarding a possible default would make significant disruptions in financial markets increasingly probable” and that “such financial market disruptions would very likely be coupled with declines in the price of equities, a loss of consumer and business confidence, and a contraction in access to private credit markets.”
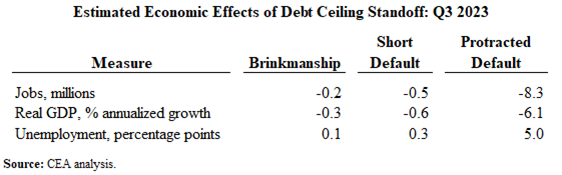
In fact, we have already seen evidence of significant market stress correlated with debt ceiling tensions. Yields on Treasury bills with maturity dates around the X-date have increased considerably—directly increasing the cost of borrowing for the government and thus the cost to taxpayers. Figure 1 below demonstrates this; since the middle of April, yields on short-duration Treasury bills around the expected X-date have increased by nearly 1 percentage point, or roughly 20 percent.
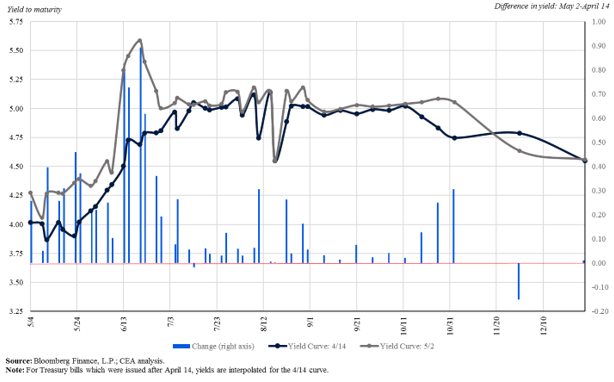
The cost of insuring U.S. debt has also risen substantially and is now at an all-time high, reflecting increased worries about a U.S. default. In fact, credit default swap (CDS) spreads—the insurance premiums that must be paid to insure U.S. debt—started to increase dramatically in April, as demonstrated by Figure 2 below.
The closer the U.S. gets to the debt ceiling, the more we expect these market-stress indicators to worsen, leading to increased volatility in equity and corporate bond markets and inhibiting firms’ ability to finance themselves and engage in the productive investment that is essential for extending the current expansion.
Risks of a brief default
Should we breach the debt ceiling, the costs to the economy would be likely to be quickly felt. Mark Zandi, Chief Economist of Moody’s Analytics, predicted that even with a brief default, a “crisis, characterized by spiking interest rates and plunging equity prices, would be ignited. Short-term funding markets, which are essential to the flow of credit that helps finance the economy’s day-to-day activities, likely would shut down as well.” Right after a default, Fitch Ratings reports that “the US’s rating would be moved to “‘RD’ (Restricted Default) [and] affected Treasury securities would carry a ‘D’ rating until the default was cured.”
According to Moody’s, even a short debt limit breach could lead to a decline in real GDP, nearly 2 million lost jobs, and an increase in the unemployment rate to nearly 5 percent from its current level of 3.5 percent. Moody’s also notes that even a short debt limit breach could lead to lastingly higher interest costs: “If Treasury securities are no longer perceived as risk-free by global investors, future generations of Americans would pay a steep economic price.” A Brookings analysis noted that losing the unparalleled safety and liquidity of the Treasury market due to default could translate into over $750 billion in higher federal borrowing costs over the next decade. Peterson Institute economists have argued that lower demand for Treasuries would weaken the dollar’s role in the global economy: “This weakening of official dollar purchases would likely increase volatility in the dollar’s value against other currencies and decrease liquidity, prompting investors to reduce their holdings of dollars in any form.”
Risks of a protracted default
The costs would be even greater under a protracted default. A CEA simulation of the effect of a protracted default (Figure 3) shows an immediate, sharp recession on the order of the Great Recession.[1] In 2023 Q3, the first full quarter of the simulated debt ceiling breach, the stock market plummets 45 percent, leading to a hit to retirement accounts; meanwhile, consumer and business confidence take substantial hits, leading to a pullback in consumption and investment. Unemployment increases 5 percentage points as consumers cut consumption, and businesses lay off workers. Unlike the Great Recession and the COVID recession, the government is unable to help consumers and businesses. As the breach continues, the economy heals slowly, and unemployment is still 3 percentage points higher at the end of 2023.
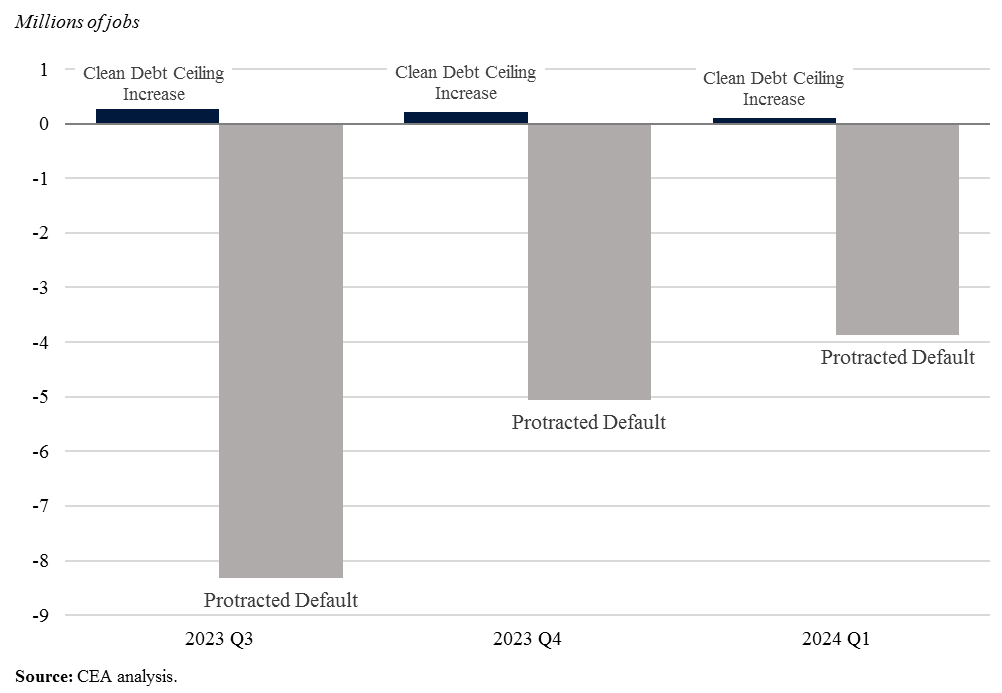
A recent analysis by Moody’s, using a different model of the macroeconomy, arrived at a similar conclusion. They predict that under a clean debt ceiling increase, job growth continues over the next few quarters, adding 900,000 jobs. But under a protracted default scenario, job losses amount to almost 8 million, an extremely stark difference of similar magnitudes to our own modeling.
Without the ability to spend on counter-cyclical measures such as extended unemployment insurance, Federal and state governments would be hamstrung in responding to this turmoil and unable to buffer households from the impacts. Neither would households be able to borrow through the private sector as the interest rates on the financial instruments that households and businesses use—Treasury bonds, mortgages, and credit card interest rates—would skyrocket due to risks of an uncertain future.
While policy makers have thus far, in the long history of our Nation, avoided inflicting such damage on the American and even global economies, virtually every analysis we have seen finds that default leads to deep, immediate recessionary conditions. Economists may not agree on much, but when it comes to the magnitude of risks invoked by closely approaching or breaching the debt ceiling, we share this deeply troubling consensus.
[1] The CEA simulation was done using FRB/US assuming negative shocks to consumer and business confidence that mimic those experienced during the Great Recession, increased interest rate premiums, and 20-30 percent cutbacks in government spending. Given the current elevated level of inflation, the Taylor rule-governed federal funds rate reacts slowly to the economic calamity.

